By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on February 22, 2016

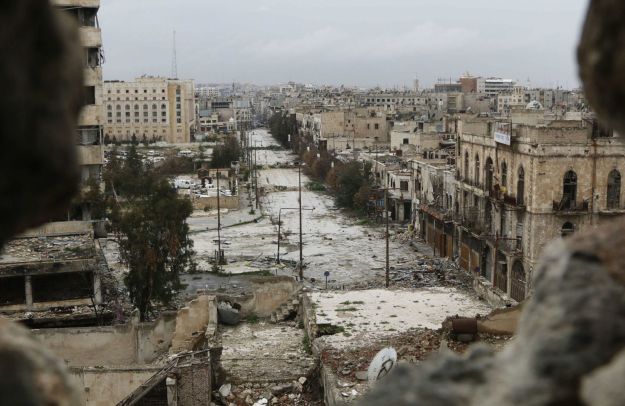
Aleppo City after the destruction of the Asad regime, Iran, and Russia
Introduction
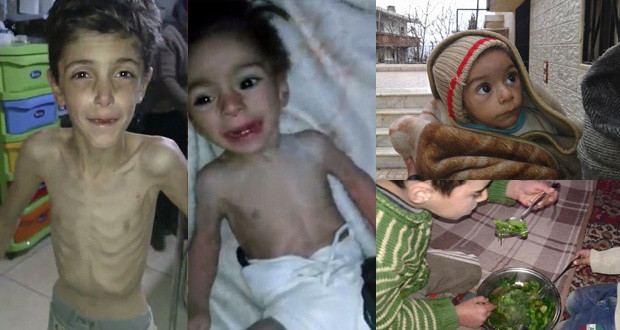
From the beginning of Syria’s war, the regime of Bashar al-Assad, enabled by Iran and Russia, has run a very elaborate media war to portray itself as the victim of an international conspiracy, wherein its only opponents are terrorists from al-Qaeda and its offshoots who are being used by foreigners—namely the Gulf States, Turkey, Israel, and the United States—to overthrow a defiant “resistance” State.
The other part of this strategic messaging is aimed at the West, which Assad otherwise accuses of supporting jihadi-Salafist terrorism against him: Assad is the only alternative to the terrorists, it says, so the West should support him. War criminal he might be, he will protect the minorities—his role in endangering them by starting a sectarian war against the Sunni majority and bolstering the takfiris within the insurgency to cannibalize all legitimate or engageable armed opposition, notwithstanding—and has no immediate plans to fly planes into Western skyscrapers. (That the leading edge of Assad’s ground forces are made up of radically sectarian, foreign Shi’a jihadists under Iran’s control, some of them Iraqis responsible for killing a quarter of the 4,000 U.S. soldiers who fell in Mesopotamia, and are integrated into a State-run terrorist network that has struck Western and Jewish targets the world over, gets left out.)
For Assad and his allies, it helps if this propaganda is not only delivered by regime spokesman but independent analysts, journalists, academics, and politicians. In the last ten days two salient examples have emerged: Stephen Kinzer, a veteran journalist, including for The New York Times, who wrote in The Boston Globe, and Jeffrey Sachs, an academic economist working at Columbia University, who wrote in The Huffington Post. Mixing together conspiracy theories, half-truths, and outright lies—disinformation, to give it an old name—both Kinzer and Sachs told a version of the regime’s narrative. Why they did this is best-known to them. Continue reading →