By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 17 August 2017

I released a report today, published by the Henry Jackson Society, The Forgotten Foreign Fighters: The PKK in Syria. Continue reading
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 17 August 2017

I released a report today, published by the Henry Jackson Society, The Forgotten Foreign Fighters: The PKK in Syria. Continue reading
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 16 August 2017

Recep Tayyip Erdogan (image source)
The Turkish government has gotten more and more deeply involved in Syria since the uprising began in 2011. But Turkey now finds its original aim, namely the overthrow of Bashar al-Assad’s regime, unattainable, creating tensions with the Syrian armed opposition, its primary lever inside Syria, and there are considerable problems stabilizing the zone of Syria that came under Turkish occupation after Ankara’s direct intervention in 2016. The defeat of Turkey’s primary objective has been accompanied by the rise of further problems, notably the exacerbation of its longest-standing internal security threat, that posed by the Kurdistan Workers’ Party (Partiya Karkerên Kurdistan – PKK), and the generation of new internal threats, from the Islamic State (IS) and potentially from al-Qaeda-linked groups. The options for solving these problems are constrained and unpalatable. Continue reading
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 31 July 2017

Earlier this month, it was announced that an LGBT military unit had been formed to fight the Islamic State (IS) in its Syrian “capital”, Raqqa city. There does appear to be such a unit in existence, though it is militarily inconsequential and likely has fewer than a dozen members, all of them foreign. The unit’s primary intention was to bolster the ongoing media-political campaign of the Kurdistan Workers’ Party (PKK), which is selling itself to Western audiences as a “progressive” ideological ally in the Middle East. This is the latest chapter in a conflict where the significance of the media war has few precedents. Continue reading
Originally published at The Henry Jackson Society
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 9 July 2017

Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) logo
The offensive to expel the Islamic State (IS) from its primary urban stronghold in Syria, Raqqa city, began on 6 November 2016 with shaping operations and commenced in earnest on 6 June 2017. Backed by the U.S.-led Coalition, the operation, known as EUPHRATES WRATH, is being carried out on the ground by the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) or Quwwat Suriya al-Dimoqratiyya (QSD). The SDF is formally a coalition of Kurds and Arabs—its announcement of the Raqqa operation named eighteen distinct sub-units. But the predominant force within the SDF is the Kurdistan Workers Party (PKK), and the Arab SDF play a “secondary role of maintaining local security,” which is to say providing an acceptable face for the PKK’s administration in the Arab-majority areas it has captured. Examining the SDF’s composition, and the recent marginalization of Arab SDF groups, underscores the point. Continue reading
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 7 July 2017

Announcement of the Kurdish Salvation Movement, 12 March 2017
As the operation proceeds to expel the Islamic State (IS) from its last major Syrian urban stronghold, Raqqa city, a statement was published on 5 July by a number of clerics, which points to the danger that the Coalition campaign, by partnering exclusively with Kurdish forces, is preparing conditions that will allow other Islamists to fill the vacuum after IS loses overt control of eastern Syria.
Continue reading
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 24 June 2017
Al-Naba 84, page 3
The Islamic State (IS) has a standard strategy of withdrawing from urban areas and conserving its forces when faced with an overwhelming enemy. This strategy has been publicly spelled out by IS, more recently and a decade ago when “the State” was new. The notable exceptions to this rule, Fallujah (2004) and Kobani (2014), were driven by political considerations, and it appears that such considerations apply to Raqqa, IS’s Syrian “capital”, which came under attack from the U.S.-led Coalition’s “partner force”, the PKK front-group that calls itself the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF), on 6 June. In the 84th edition of IS’s weekly newsletter, Al-Naba, released on 8 June, the main editorial was about the Raqqa battle and encouraged IS’s jihadists to fight to the very last, ostensibly to inflict such heavy casualties over such a protracted period that the SDF/PKK would not be able to sustain itself. Continue reading
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 19 June 2017
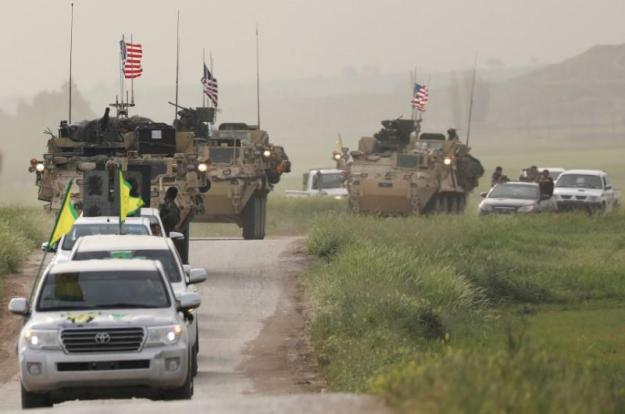

YPG and U.S military vehicles in Darbasiya, northern Syria, 28 April 2017. REUTERS/Rodi Said/File Photo
At the end of May, Christoph Reuter, a journalist with Der Spiegel, embedded with the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) as it made its way, supported by the U.S.-led Coalition, toward Raqqa city, the Syrian “capital” of the Islamic State’s (IS) caliphate. Reuter’s report provides snapshots of a number of important—and worrying—dynamics at play that have made the U.S. decision to back the SDF to liberate Raqqa so worrying over the long-term, even on its own terms as a means of sustainably defeating IS. Continue reading
Originally published at The Henry Jackson Society
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 8 June 2017

Aftermath of a TAK bombing in central Istanbul, Turkey, 7 June 2016
The Kurdistan Freedom Falcons (TAK) issued a threat against Turkey on Tuesday, at the very moment the U.S.-led Coalition was announcing the commencement of the operation to evict the Islamic State (IS) from its Syrian capital, Raqqa, in alliance with the TAK’s mother organization, the Kurdistan Workers’ Party (PKK). This underlines some of the challenges confronting the Coalition as a result of a half-decade of short-sighted counter-terrorism policy in Syria and a regional posture that tilted away from traditional allies. Continue reading
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 6 June 2017

A member of the YPG/PKK militia, Delil Souleiman/Agence France-Presse — Getty Images
The United States recently committed itself to arming the Kurdish People’s Protection Units, known as the Y.P.G., to help evict the Islamic State from its Syrian stronghold, Raqqa. This decision is likely to prove deeply troublesome, risking the regional stability necessary for the lasting defeat of the Islamic State.
The Y.P.G. denies that it is, in effect, a wing of the Kurdistan Workers’ Party, or P.K.K., but the evidence is clear. The P.K.K., a Marxist-leaning Kurdish nationalist organization, was founded in Turkey in 1978, and took up arms against the Turkish state in 1984. The group’s leader, Abdullah Ocalan, was expelled from Syria in 1998, when his old patron, the regime of Hafez al-Assad (Bashar’s father), came under military threat from Turkey. Mr. Ocalan was soon arrested by the Turks, and the tide of war turned against the P.K.K. Continue reading
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 30 May 2017
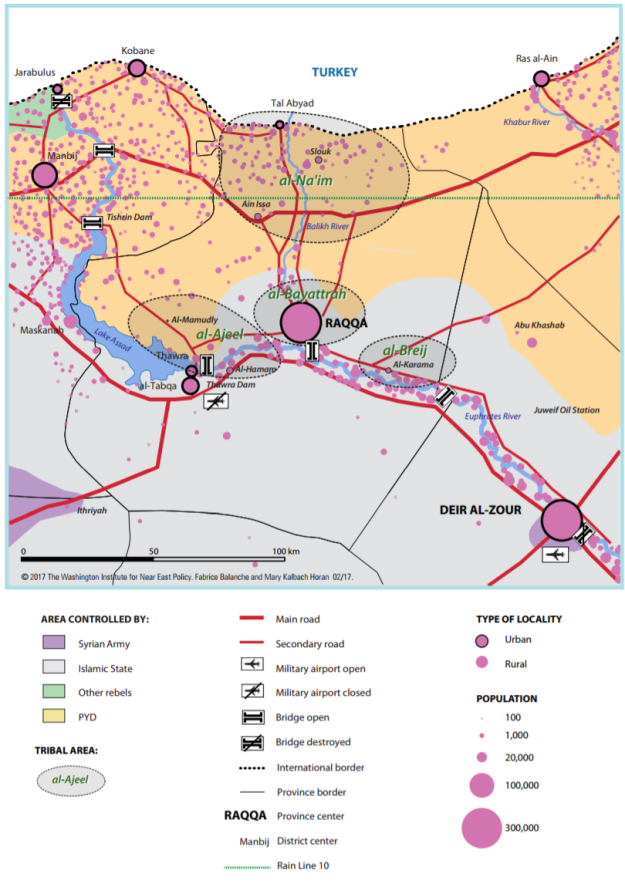
Map of the tribes around Raqqa city (source: WINEP report)
We are now on the eve of the operation to evict the Islamic State (IS) from its Syrian capital, Raqqa, and, as expected, the United States will partner with the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF), the front-group for the Democratic Union Party (PYD) and its armed wing, the People’s Protection Units (YPG), which President Donald Trump’s administration has committed to directly arming.
Many of the doubts voiced about this course relate to Turkey, since the PYD/YPG is—despite continued efforts to obfuscate the fact—the Syrian department of the Kurdistan Workers’ Party (PKK), the premier internal security threat to Turkey for many decades. The discussion then tends to fall into one of two grooves. Continue reading