By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 11 January 2025
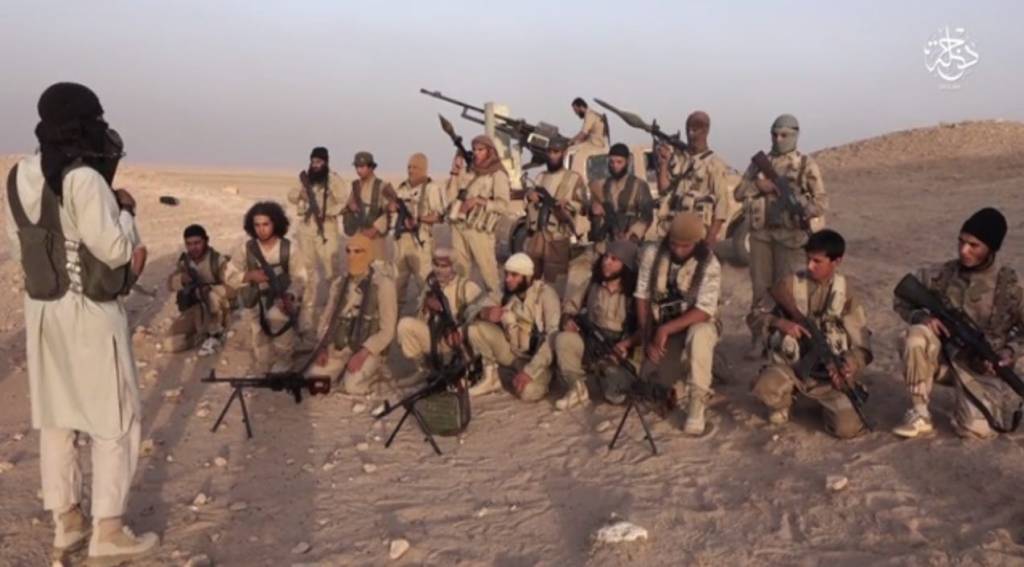

By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 7 September 2021

Anti-Taliban fighters watch U.S. airstrikes at Tora Bora, 16 December 2001 || REUTERS/Erik de Castro
The State Department spokesman Ned Price said, on 27 August, “The Taliban and the Haqqani Network are separate entities”. The next day, the Pentagon Press Secretary John Kirby slightly modulated this, having first tried to dismiss the question, by conceding there was “a certain amount of … commingling … there’s a marbling … of Taliban and Haqqani”, before saying he was “pushing back … [on] the relevance of that discussion”.
What these officials were trying to do was two-fold: (1) to refute press reports that U.S. officials in Kabul had shared “a list of names of American citizens, green card holders, and Afghan allies” with the Taliban, amounting to having “put all those Afghans on a kill list”, as one “defense official” put it; and (2) to deny that the U.S. coordination with the Taliban to evacuate people the jihadists wanted to kill—a surreal enough situation—had involved the additional political and legal problems of coordinating with a formally registered Foreign Terrorist Organization (FTO), as the Haqqani Network is. Continue reading
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on October 4, 2020

A chapter about Al-Qaeda I wrote for the American Foreign Policy Council’s (AFPC) ‘World Almanac of Islamism’ was published today. Do check it out, and the broader site, which is a great, accessible resource. The format of the website necessitated that the chapter as I submitted it was edited, condensed, and split up to fill out the various categories. In case it is of any interest, the original version of the chapter is reproduced below.
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 26 May 2020

Early in his new book, Your Sons Are At Your Service: Tunisia’s Missionaries of Jihad, The Washington Institute’s Aaron Zelin quotes a pair of sociologists who note that ‘where theories are plentiful … ideas are vacuous’. The book is in many ways the antithesis of this approach. It is not without theoretical content; where social movement theory arises as a means of understanding jihadism, say, the author gives an overview of the literature to contextualise it for the reader. But the general approach is historical, empirical, and detail-rich, so that by the time Zelin summarises his findings in the various sections there can be no doubt about the evidentiary basis. Continue reading
This article was originally published at The Brief
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 26 October 2018
At the beginning of September, New America published a paper, based on recovered al-Qaeda documents, which concluded that there was “no evidence of cooperation” between the terrorist group and the Islamic Republic of Iran. New America’s study lauds itself for taking an approach that “avoids much of the challenge of politicization” in the discussion of Iran’s relationship with al-Qaeda. This is, to put it mildly, questionable.
A narrative gained currency in certain parts of the foreign policy community during the days of the Iraq war, and gained traction since the rise of the Islamic State (IS) in 2014, that Iran can be a partner in the region, at least against (Sunni) terrorism, since Tehran shares this goal with the West. Under President Barack Obama, this notion became policy: the US moved to bring Iran’s revolutionary government in from the cold, to integrate it into the international system. Continue reading
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 5 February 2018
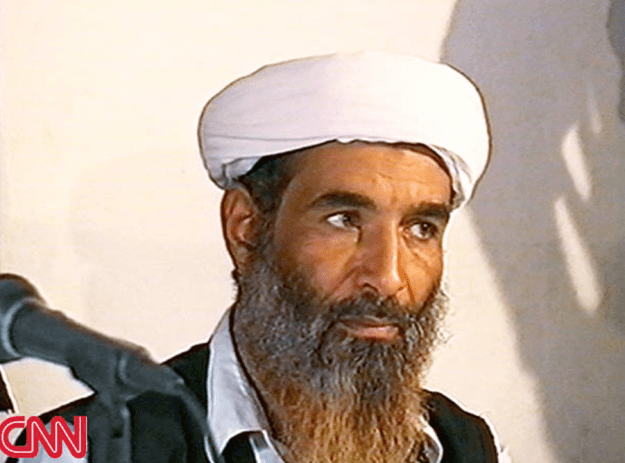

Al-Qaeda’s military leader Muhammad Atef at a press conference in Afghanistan, 26 May 1998 (image source: CNN)
Muhammad Atef, best-known as Abu Hafs al-Masri, but who also went by the names Taseer Abdullah or Taysir Abdullah and Subhi Abu Sitta, was al-Qaeda’s military leader between 1996 and 2001, and one of the three people most responsible for the terrorist attack in the United States on 11 September 2001. Continue reading