By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 30 April 2025

By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 8 November 2018
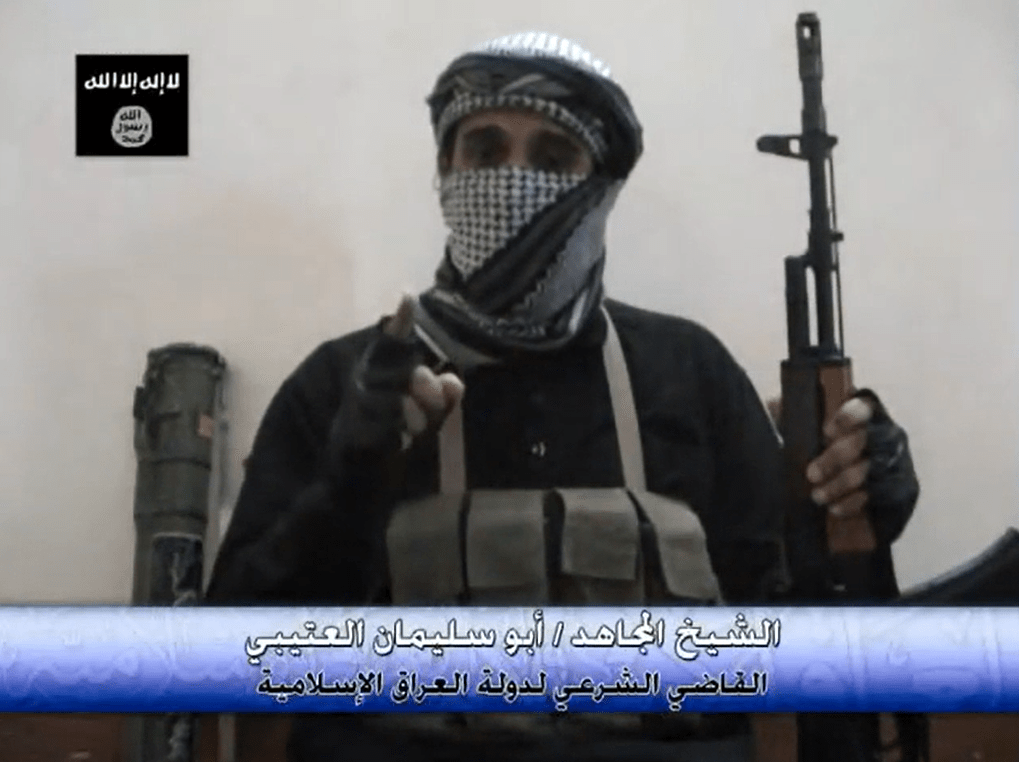
As explained in a previous post, Abu Sulayman al-Utaybi, the Chief Judge of the Islamic State of Iraq (ISI) from early April to late August 2007, has become an important character in many accounts of the history of the Islamic State movement because his abrupt removal from office was followed by his defection from ISI and a journey to Al-Qaeda’s central leadership in Pakistan, where he provided a testimony against his former bosses. If interested in an assessment of that testimony and the whole saga around how it has been used—by Western scholars, Al-Qaeda, and other critics of the Islamic State—check out the prior post. This post reproduces the transcript for what is, as far as I can tell, Abu Sulayman’s first media product for ISI, a twenty-minute video speech released by Al-Furqan Foundation for Media Production on 11 April 2007, entitled, “Why Do We Wage Jihad?”
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 7 November 2018

On 24 November 2013, the day after Al-Qaeda leaked the full testimony of Abu Sulayman al-Utaybi, the chief judge of the Islamic State (IS) who made various charges against the leadership after he defected in 2007, a pro-IS response was issued, signed by one Mu’awiya al-Qahtani, entitled, “Refutation of the Letter Attributed to the Judge Abu Sulayman al-Utaybi—May God Accept Him—with Evidence and Proofs”. A translation of Al-Qahtani’s document is given below.
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 6 November 2018
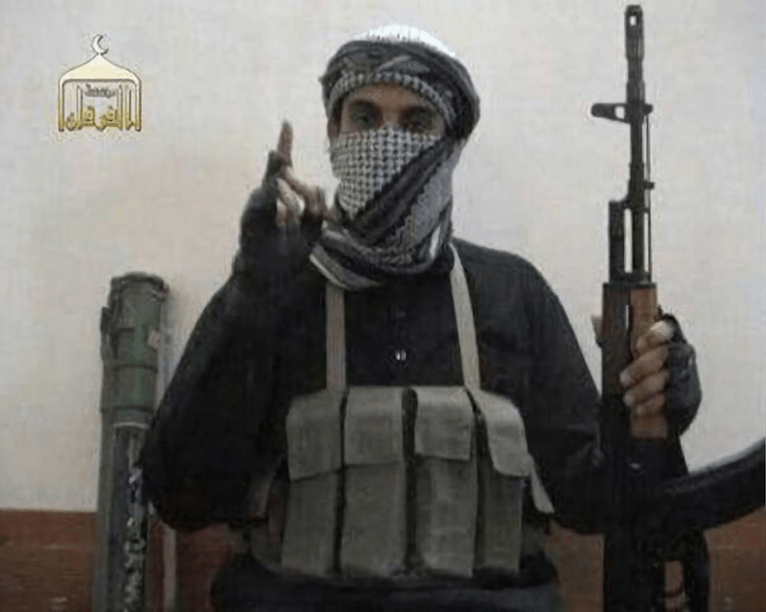

Abu Sulayman al-Utaybi, a Saudi who abandoned his Islamic studies to journey to Iraq in 2006, was appointed chief judge, of the Islamic State movement in March 2007, six months after the Statehood declaration. Between April and June 2007, Abu Sulayman released some public sermons—the picture above is from the first—for what was then called the Islamic State of Iraq (ISI), which had publicly dissolved its bonds to Al-Qaeda when it became a “State” in October 2006, while in fact retaining its bay’a (oath of allegiance) to Al-Qaeda in private.
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 17 March 2018

A video statement was put out on 15 October 2006 by the official spokesman of what was then called the Mujahideen Shura Council (al-Majlis Shura al-Mujahideen or MSM), the entity in which Al-Qaeda in Iraq (AQI) had nominally subsumed itself in January 2006, announcing the creation of the Islamic State of Iraq (ISI). The MSM spokesman, Muharib al-Jubouri, seen above, who had not been in the job long—the first AQI/MSM spokesman, Abu Maysara al-Iraqi, had been killed a few months earlier—was now the ISI spokesman,[1] and his speech made clear that a coalition of tribesmen and insurgents announced by MSM three days earlier, the Alliance of the Scented Ones (Hilf al-Mutayibeen), was also incorporated in this “State”. The transcript of Muharib’s speech, entitled (unimaginatively enough), “Announcement on the Establishment of the Islamic State of Iraq”, is translated below.
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 5 February 2018

Usama bin Ladin in an al-Qaeda video (image source: CNN)
A letter released by the Office of the Director of National Intelligence (ODNI) on 20 May 2015, the “Letter to Abu Abdallah al-Hajj”, was written by an al-Qaeda leader on 17 December 2007. The letter, reproduced below with some editions in transliteration and some important sections highlighted bold, is interesting for several reasons. Continue reading
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 6 January 2018

Iraqi soldiers from the 1st Iraqi Army Division and U.S. Soldiers board a U.S. Marine Corps CH-53 Super Stallion helicopter at Camp Ramadi, 15 Nov. 2015 (DoD photo by Staff Sgt. Daniel St. Pierre, U.S. Air Force)
The leader of the Islamic State (IS) when it was declared in October 2006 was Hamid al-Zawi (Abu Umar al-Baghdadi). Al-Zawi was killed in April 2010 and replaced in May 2010 by the current leader of the IS movement, Ibrahim al-Badri (Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi), who more explicitly embraced the title of “caliph”. On 12 May 2009, al-Zawi gave his seventeenth speech, entitled Umala Kadhabun (عملاء كذابون), which translates to something like “Lying Agents” or “Deceitful Spies”. The speech was released by IS’s Al-Furqan Media Productions and a translation was made by a pro-IS online outlet, The Jihadist Media Elite. The transcript is reproduced below. Continue reading
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 17 July 2017
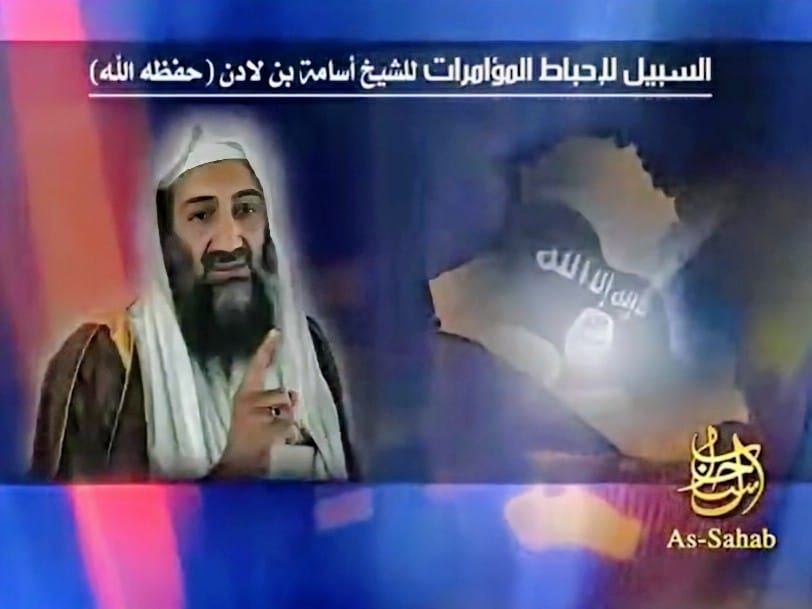
Usama bin Laden gave a speech lasting nearly an hour on 29 December 2007, entitled, “The Way to Foil the Conspiracies”. A translation of the speech is published below.
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on January 27, 2017

The Islamic State’s June 2014 declaration that the areas it controlled were the restored “Caliphate” was seen by many as a novel development. In fact, “the State” was declared in October 2006. The next month, the predecessor of the Islamic State (IS), Al-Qaeda in Mesopotamia (AQM), dissolved itself, and a month after that the claim to statehood was expanded upon—while being wilfully ambiguous about the caliphal pretensions—in the first speech by the then-emir, Hamid al-Zawi (Abu Umar al-Baghdadi). Similarly, though confusion remains on the point, it was in this same period that the symbol of the Islamic State, its black flag, was established.
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on November 5, 2015
Published at NOW Lebanon.
William McCants’ The ISIS Apocalypse: The History, Strategy, and Doomsday Vision of the Islamic State is an immensely readable addition to the literature on the most powerful terrorist-insurgent group in the world. McCants covers the Islamic State, often referred to as ISIS, from its inception in Taliban Afghanistan in 1999 to its migration to Iraq in 2002, and through its various stages before its blitzkrieg from Syria across central Iraq in June 2014, which brought ISIS to global attention. McCants shows that ISIS’s evolution is not just a religio-socio-political and military phenomenon, but an intellectual one. ISIS has built the foundations of its statelet on the lessons learned by Salafi-jihadists from their previous battlefronts, such as Afghanistan, Chechnya, and Algeria, and their various mistakes, many of them ISIS’s own. Continue reading