By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 11 January 2025
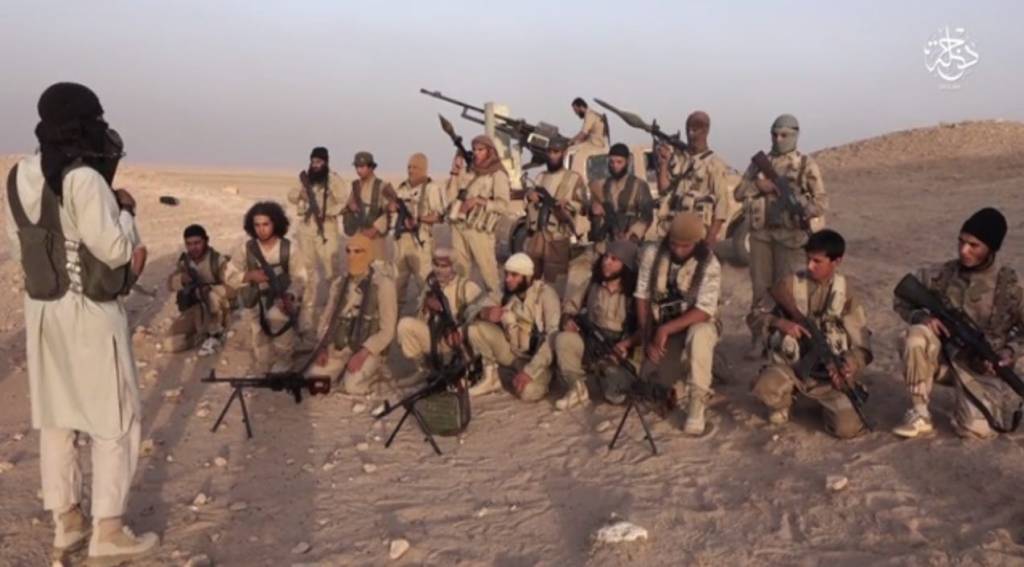

By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 24 August 2022
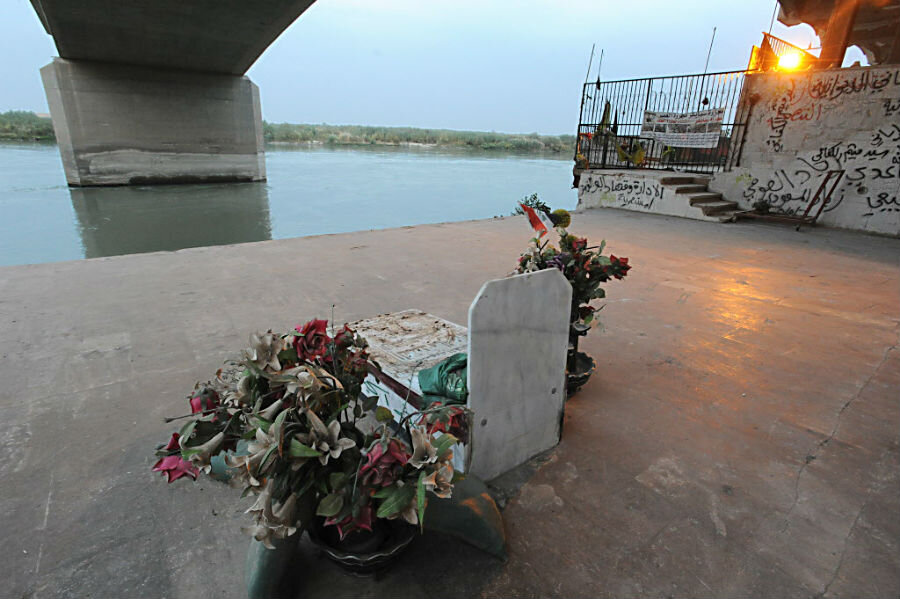
Area on the banks of the Tigris where the cadets of Camp Speicher were massacred by the Islamic State || Scott Peterson/The Christian Science Monitor
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 18 June 2022

A U.S. helicopter above the American Embassy in Kabul, 15 August 2021 | AP
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 28 December 2019

In a long article last week, I looked at why the U.S. ran a formal occupation of Iraq for fourteen months after the fall of Saddam Husayn in April 2003, given that there had been an explicit pre-invasion decision not to have an occupation government. The short answer is that the occupation was installed through deception by the State Department, supported by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). State and CIA had argued for a protracted occupation in the Situation Room debates in 2002, but President George W. Bush had sided with the Pentagon, which advocated a rapid transfer of power to Iraqis. Having lost in the formal inter-agency process, the State Department succeeded by subversion in getting its way on the ground in Iraq. The disaster this caused in the mismanagement of post-Saddam Iraq was, as the article explained in detail, only the most serious impact of the toxic schism between State/CIA and the Pentagon, a factor whose import is difficult to overstate when examining how the Bush administration functioned. (This feud also at times drew in the Vice President’s Office, which tended to support the Pentagon.)
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 19 November 2019

President Barack Obama meeting President-elect Donald Trump, 10 November 2016 [image source]
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 18 November 2019

“SDF commander “General Mazlum Kobani” (the PKK executive official Ferhat Abdi Shahin) being interviewed by AFP in Hasaka city, 24 January 2019 [image source]
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 16 February 2019

Front page Al-Naba 169
The Islamic State (IS) released the 169th edition of its newsletter, Al-Naba, on 14 February 2019. Al-Naba 169 leads with the attack on the governor of Borno in Nigeria by IS’s branch in that country. In terms of volume, much of the focus remains on the guerrilla campaign in Iraq and Syria, though there is an item on the last stand of the caliphate in Baghuz, the final village in eastern Syria. IS highlights its clashes with al-Qaeda in Yemen. There is a profile of a Russian-speaking atheist-turned-jihadist who was killed in Egypt. And perhaps most notable is an essay on Saudi Arabia, where IS has a terrorist infrastructure that is instructed to be patient. It is a question that likely is unanswerable until it is too late how strong IS is in Saudi Arabia. Continue reading
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 10 December 2017

Russian soldiers in Efrin, Syria, 1 May 2017 (source)
The American-led Coalition against the Islamic State (IS) partnered with the “Syrian Democratic Forces” (SDF), a political façade for the proscribed Kurdistan Workers’ Party (PKK), as the ground force in Syria. The most ventilated problems with this partnership so far have been the strain it has put on relations with NATO ally Turkey, against which the PKK has run a terrorist-insurgency for more than thirty years, and the deep local suspicion of the PKK’s governing program that might yet reverse the gains against IS and open political space for other jihadists like al-Qaeda. Another of the problems is now gaining salience: the PKK’s long-term alliance with Bashar al-Asad’s regime and the states—Russia and Iran—that keep it alive. Continue reading