By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 29 April 2018
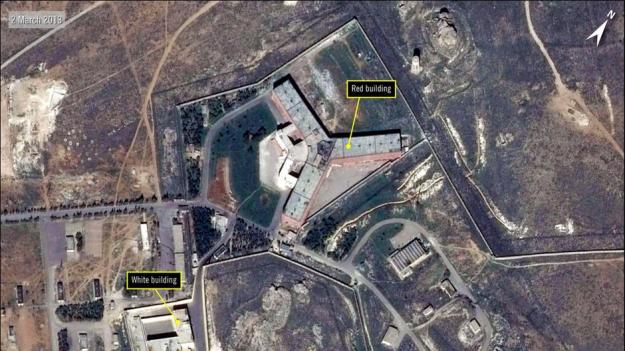
A satellite image of Sednaya prison, about 20 miles north-east of the presidential palace. CNES and ASTRIUM / Amnesty International via AFP
To accompany the release of “Syria’s Slaughterhouses”, a film by TRT World’s “Off The Grid”, I was asked to give an overview of the available evidence of the Assad regime’s crimes against humanity.
The launching of a limited punitive raid against the Syrian regime of Bashar al Assad for the use of poison gas has brought some attention to the regime’s crimes. The regime’s visible crimes are numerous and devastating.
In addition to using weapons of mass destruction, fighter jets have levelled ancient cities, sieges have starved populations into submission, and improvised explosives like barrel bombs have maimed thousands. These tactics are part of what UN investigators have called a “systematic and widespread attack against [the Syrian] civilian population”.
The UN commission recently noted that what the Assad regime has done amounts to crimes against humanity, including extermination, murder, rape, and torture.
What does not get enough attention is the part of Assad’s criminality that is most difficult to see: that which takes place in the prisons, a vast network of concentration camps where torture and murder is routine. Continue reading →