By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 16 August 2022
Tag Archives: Prophet Muhammad
Britain’s Latest Surrender to its Unspoken Islamic Blasphemy Law
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 13 June 2022

Muslim protesters outside the Cineworld in Birmingham demand ‘The Lady of Heaven’ film is banned, 5 June 2022 [image source]
Islamic State Wants the War Against Israel to Be Religious, Not Nationalist
Islamic State Bids Farewell to the Caliph
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 10 November 2019
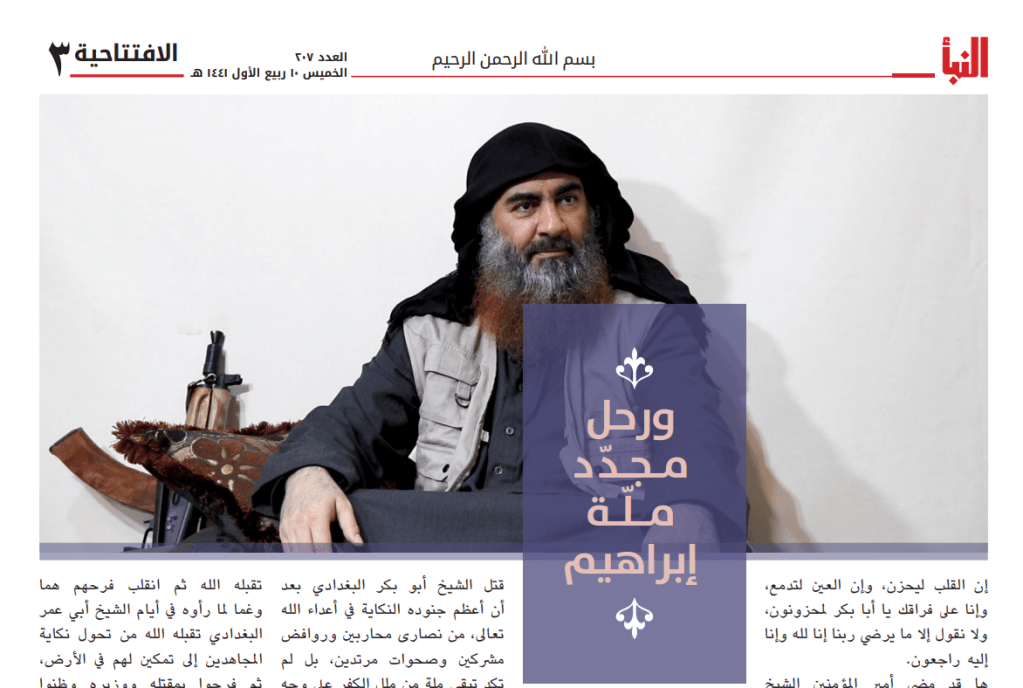
The 207th edition of Al-Naba, the weekly newsletter of the Islamic State (IS), published on 7 November 2019, devotes its main editorial to Ibrahim al-Badri (Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi), the first “Caliph” when the “Caliphate” was declared in June 2014, who was killed on 27 October 2019.
Another Product of “Londonistan”: Abdullah Ibrahim al-Faisal
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on 8 December 2017

Abdullah al-Faisal
The U.S. Treasury Department sanctioned Abdullah Ibrahim al-Faisal (born: Trevor William Forrest), a Jamaican cleric who supports the Islamic State (IS) on 5 December. This was long overdue. Al-Faisal’s record of disseminating jihadist ideology, and influencing and/or interacting with terrorists, goes back several decades. And since 2014, al-Faisal has been one of IS’s influential English-language propagandist-recruiters. Continue reading
The Flag of the Islamic State
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on January 27, 2017

The Islamic State’s June 2014 declaration that the areas it controlled were the restored “Caliphate” was seen by many as a novel development. In fact, “the State” was declared in October 2006. The next month, the predecessor of the Islamic State (IS), Al-Qaeda in Mesopotamia (AQM), dissolved itself, and a month after that the claim to statehood was expanded upon—while being wilfully ambiguous about the caliphal pretensions—in the first speech by the then-emir, Hamid al-Zawi (Abu Umar al-Baghdadi). Similarly, though confusion remains on the point, it was in this same period that the symbol of the Islamic State, its black flag, was established.
Islam’s First Terrorists
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on August 24, 2015
Book Review: The Assassins: A Radical Sect in Islam (1967) by Bernard Lewis
This review can be read in six parts: one, two, three, four, five, and six.
Abstract
The fourth Caliph, Ali, was assassinated during a civil war that his supporters, Shi’atu Ali (Followers of Ali), lost to the Umayyads, who thereafter moved the capital to Damascus. The Shi’a maintained that the Caliphate should have been kept in the Prophet’s family; over time this faction evolved into a sect unto themselves, which largely functioned as an official opposition, maintaining its claim to the Caliphate, but doing little about it. Several ghulat (extremist) Shi’a movements emerged that did challenge the Caliphate. One of them was the Ismailis. Calling themselves the Fatimids, the Ismailis managed to set up a rival Caliphate in Cairo from the mid-tenth century until the early twelfth century that covered most of North Africa and western Syria. A radical splinter of the Ismailis, the Nizaris, broke with the Fatimids in the late eleventh century and for the next century-and-a-half waged a campaign of terror against the Sunni order from bases in Persia and then Syria. In the late thirteenth century the Nizaris were overwhelmed by the Mongols in Persia and by the Egyptian Mameluke dynasty which halted the Mongol invasion in Syria. The Syrian-based branch of the Nizaris became known as the Assassins, and attained legendary status in the West after they murdered several Crusader officials in the Levant. Attention has often turned back to the Assassins in the West when terrorist groups from the Middle East are in the news, but in the contemporary case of the Islamic State (ISIS) the lessons the Nizaris can provide are limited. Continue reading
Islam’s First Terrorists, Part 1
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on August 17, 2015
Book Review: The Assassins: A Radical Sect in Islam (1967) by Bernard Lewis
Abstract
The fourth Caliph, Ali, was assassinated during a civil war that his supporters, Shi’atu Ali (Followers of Ali), lost to the Umayyads, who thereafter moved the capital to Damascus. The Shi’a maintained that the Caliphate should have been kept in the Prophet’s family; over time this faction evolved into a sect unto themselves, which largely functioned as an official opposition, maintaining its claim to the Caliphate, but doing little about it. Several ghulat (extremist) Shi’a movements emerged that did challenge the Caliphate. One of them was the Ismailis. Calling themselves the Fatimids, the Ismailis managed to set up a rival Caliphate in Cairo from the mid-tenth century until the early twelfth century that covered most of North Africa and western Syria. A radical splinter of the Ismailis, the Nizaris, broke with the Fatimids in the late eleventh century and for the next century-and-a-half waged a campaign of terror against the Sunni order from bases in Persia and then Syria. In the late thirteenth century the Nizaris were overwhelmed by the Mongols in Persia and by the Egyptian Mameluke dynasty which halted the Mongol invasion in Syria. The Syrian-based branch of the Nizaris became known as the Assassins, and attained legendary status in the West after they murdered several Crusader officials in the Levant. Attention has often turned back to the Assassins in the West when terrorist groups from the Middle East are in the news, but in the contemporary case of the Islamic State (ISIS) the lessons the Nizaris can provide are limited. Continue reading
Islamic State Claims the Attack on Muhammad Cartoon Event in Texas
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on May 22, 2015

Dabiq 9, page 4
The Islamic State released the ninth edition of Dabiq, its English-language magazine, on May 21, 2015. The Foreword, on pages 3 and 4, claims “credit” for the attempted terrorist attack against in Garland, Texas, on May 3. The two would-be killers, Elton Simpson and Nadir Hamid Soofi, were killed outside the Curtis Culwell Center, which was hosting a “draw (Prophet) Muhammad” cartoon contest, led by anti-Islam activist Pamela Geller, who was among the primary targets of the attack. The attack had been guided by Islamic State operative Junaid Hussain, a British hacker. The article is reproduced below with some edits for transliteration. Continue reading
Book Review: Introduction to the Qur’an (1953) by Richard Bell
By Kyle Orton (@KyleWOrton) on January 13, 2015
Richard Bell’s Introduction to the Qur’an is, at less than 200 pages, a brief and easily-digestible explanation of the context in which Islam’s “holy” book arose, and the problems of reconciling theological orthodoxy with historical accuracy. More than six decades after publication, the book remains influential in scholarship of the Qur’an. Continue reading


